Sometimes, you need to create and manipulate a two-dimensional (2D) array or a matrix. In JavaScript, an array of arrays can be used as a 2D array.
1 | const mat = [ |
How do you implement if you initialize m x n matrix with zeros?
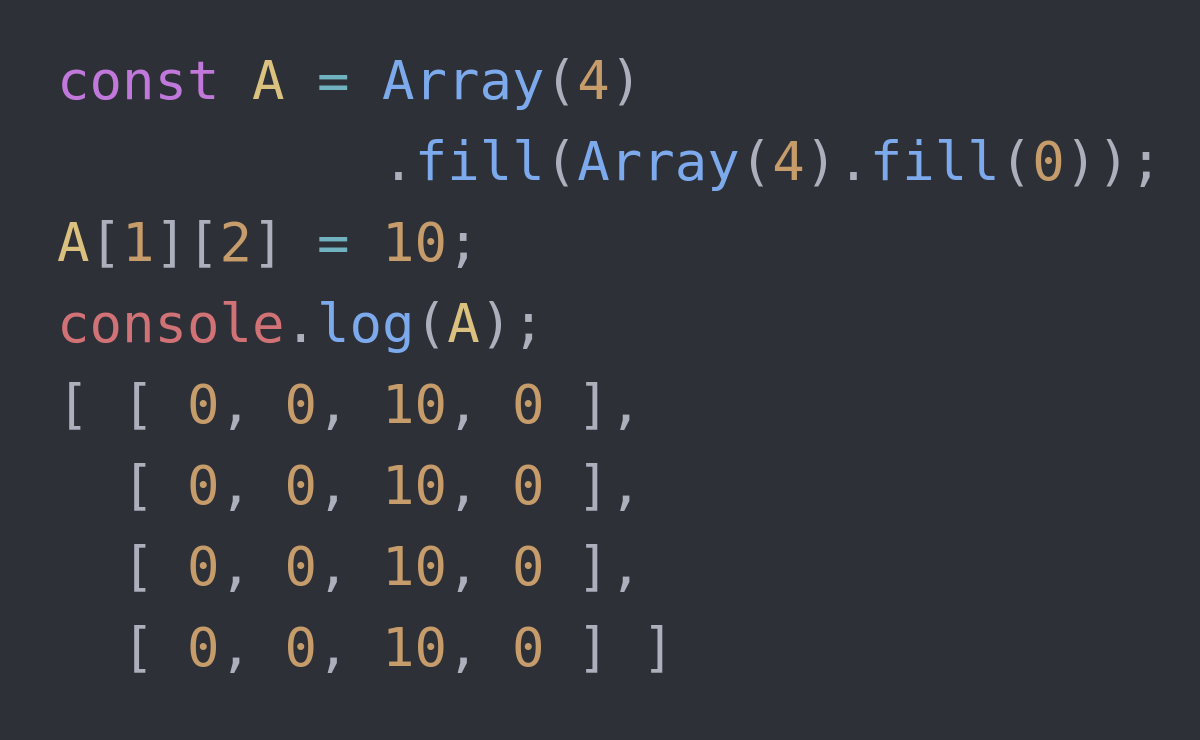
If you know about Array.prototype.fill(), you may be tempted to initialize m x n array like Array(m).fill(Array(n).fill(0)), but this does not work properly.
Since the Array(n).fill(0) creates just one array of size n and all the elements of the first array, that represents rows, point to the same, the second array as follows:
When you got to know Array.prototype.fill() method, you may be tempted to initialize m x n array like Array(m).fill(Array(n).fill(0)), but this does not work properly. Since the Array(n).fill(0) creates just one array of size n and all the elements of the first array, that represents rows, point to the same, second array as follows:
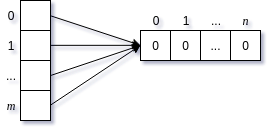
For the same reason, “Array(m).fill([])” also does not work properly.
Solutions
Initialize each row using for loop
The simplest solution is to create each row using for loop:
1 | const mat = Array(m); |
Using map
If you are aware of functional programming, you would know that a for loop can be converted to map and/or reduce. In this case, we can use a map function in this way.
1 | const mat = Array(m).fill(null).map(() => Array(n).fill(0)); |
Using Array.from()
Array.from can create using arrayLike object and map function.
It can simplify Array(m).fill(null) part of previous solution.
1 | const mat = Array.from({length:m}, () => Array(n).fill(0)); |